Can you agree? As we navigate the tech age – ok maybe we struggle through it -- we’re realizing that artificial intelligence (AI) is paving the way for better legal operations. Specifically, we must keep pace with better contracting processes. But is the “map” for paving the way so easy to follow? Can we test whether we are taking the smartest route possible? What is our “craze” for opportunity? Where does legal fit in? I’ll make no attempt to fully answer those questions, but I believe I can give us food for thought for nudging closer to specific answers.
Our craze for opportunity cannot be stopped – how come?
We’re hungry! And competitive! Businesses across industries have swiftly and most recently embraced AI to optimize business processes. It has been an interesting journey of head-scratching conundrums. According to an MIT Sloan Management Review study1, over 80 percent of companies view AI as a source of strategic opportunity, and 85 percent of companies view AI to attain competitive advantage.1This number is sure to increase as machine learning and natural language processing develop exponentially.
We’re aggressive! The craze of AI for business process development sees organizations investing significant time and resources. A collection of surveys from Harvard Business Review2 indicates that up to one-third of large companies within the United States are pursuing artificial intelligence “quite aggressively” – with thousands of projects involving business AI currently in progress. (See Davenport et al., 2019). 2
We’re expanding! Common artificial intelligence use cases allow businesses to enhance decision making, improve operational procedures, and expand the functioning of services and products.
If we’re not proactive, we’re failing! The goal of AI is not to replace business professionals – but rather to automate monotonous processes so that business professionals can focus on proactive decision-making initiatives. In this new age of business intelligence, business professionals should brace themselves to work alongside AI tools to add value to their efforts.
OK, we know that much. So, what’s the next question?
The Contract AI craze jumpstarts legal ambitions – how so?
AI-based contract management software3 can support strategic opportunities and competitive advantages for companies looking to better manage their contracts. You can configure contract management AI to systematically analyze contracts originating from internal and external paper documentation. AI can help transform static documents into dynamic assets for profitabilities like these:
- increased contract awareness and oversight;
- escalated opportunity such as contract renewals; and
- improved risk management.
HOW DOES AI IMPROVE LEGAL OPERATIIONS?
Improve contract visibility
- Organizations leveraging contract artificial intelligence4 can enjoy better contract visibility thanks to helpful features.
- Automated contract data review can allow contract teams to be more confident that key data within a contract are correct.
- Risk assessments can help organizations avoid contract risk that can damage their reputation, decrease revenue, and diminish contract value.
- Intelligent contract workflows can support accountability to automate alerts and notifications for task completion.
- On-screen recommendations can present users with valuable suggestions on how to proceed with a contract.
Best of all, you can use these features on one centralized platform to take the headache out of contract management!
Contract data extraction and field mapping helps with what?
Data mining and extraction with contract AI can help give meaning to your contract data. Organizations can decrease the time it normally takes to enter new contracts into their contract software systems. They can quickly identify key data points such as dates, locations, monetary values, phone numbers, emails, counterparties, and more and map them to easy-to-understand fields.
Drag and drop contract documents allows us to do what?
AI-powered drag and drop record initiation allows users to easily import contract documents from ranging locations. Files dropped into AI-based contract management software can run through contract artificial intelligence to help us create different contract data record types.
Leading contract AI helps introduce Microsoft (MS) Word and Portable Document Format (PDF) documents to us by enabling a document Optical Character Recognition (OCR) process. At that point, contract AI can prompt contract managers to generate new contract records with intelligent field mapping or add files to existing contract record pages.
Contract intelligence users can even add multiple documents to a contract document queue for even more centralized and rapid contract management software processes (Figure 1). Companies can name their contracts and choose a contract type to enhance organization and make contract searching easy.
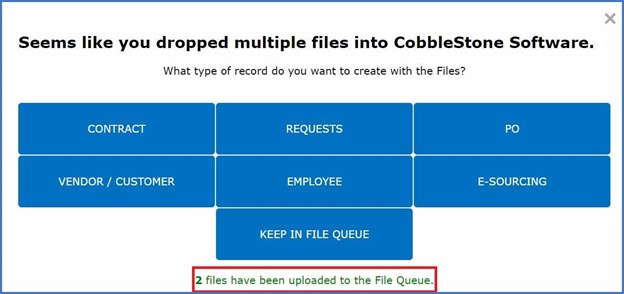
Figure 1: Contract managers can drag and drop contract documents into a file queue and quickly select the contract data field page they want to create for organized and centralized contract management.
So, can we go beyond simple contract data extraction?
Yes! Robust contract artificial intelligence can give business users the power to centrally scan their agreements and contracts to quickly locate key terms, conditions, legal phrases, and other legal text.
Contract intelligence can identify and extract text and clauses using natural language processing (NLP) with intelligent fuzzy logic matching of legal terms and phrases along with structured data recognition. NLP allows contract AI to understand the human language as it is written.
Easily manage sensitive data
Organizations can use contract AI to easily identify sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII), payment card information (PCI), vendor data, counterparty data, and more for redaction. Furthermore, rules can be configured for the categorization and protection of this data.
Perform statistical contract data analysis
Organizations can quickly and accurately determine positive, negative, or neutral aspects of a contract to assist with strategy. If a contract has a value of X% greater, than the average contract value in a contract software system, for instance, can trigger an alert containing an updated workflow process.
Improve contract clause extraction and machine learning
Intelligent clause extraction and clause identification can continuously improve with machine learning. Contract AI software users can use machine learning that finds standard clauses within a document when that document is added to contract management software.
Organizations can also add clause text to training data for further machine learning and improve future contract clause recognition. This functionality can continuously help enhance data entry accuracy and speed.
As well, contract artificial intelligence can intelligently categorize clauses into an organization’s pre-established clause types while presenting a percentage of confidence in this clause categorization (Figure 2).
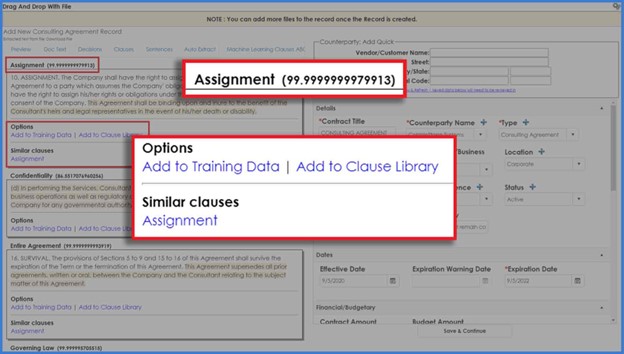
Figure 2: Contract artificial intelligence can become ever more confident in its clause categorizations with the continuous introduction of standard and unique contract clauses into contract management software.
Accelerate risk assessment and mapping
Contract risk rating and mapping features can provide insight into potential contract risk. A risk assessment matrix within AI-based contract management software displays risk probability patterns and exposure (Figure 3). This risk visibility can help organizations make informed risk decisions.
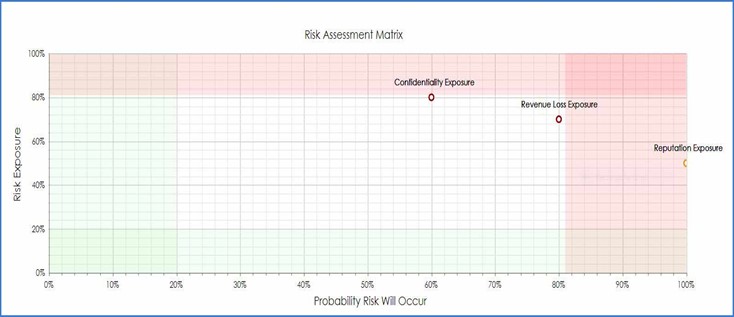
Figure 3: Contract artificial intelligence can offer a risk assessment matrix that maps risk probability and risk exposure in an organized fashion so you can increase contract risk visibility and decide how to proceed with urgent risk variables urgent before they become untenable.
Measure contract management employee accountability
Contract AI can analyze accountability with a “risk score” that measures how attentively an organization uses risk management features (Figure 4). Contract software system administrative professionals can see where employees are lacking in accountability and proceed with a revision in strategy.
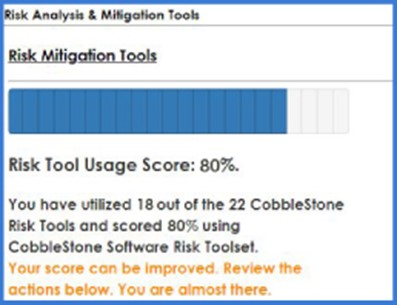
Figure 4: Contract artificial intelligence allows contract management software system administrators to analyze how many of the risk management tools at their disposal they use, as well as which risk management areas can be improved on.
For example, consider Paul’s organization. Out of the many functionalities available to his team for risk management, his organization only uses 40% of them, according to his “risk score.” In this case, Paul’s team is using less than half of their contract lifecycle management software's AI-based risk tools. As an administrator of AI-based contract administration software, Paul is prompted to improve risk management procedures with detailed insight into what his organization's process is lacking.
But, continuing with this example, suppose Paul's software system reveals that his team is not putting adequate time into tracking contract approvals – the contract review process in which parties and stakeholders route approval for contracts. Paul’s organization can adjust its approvals tracking procedures. With newfound insights, the team can allocate the proper channels to mitigate risks associated with counterparty activity during the contract approvals process.
So, why is the future of legal operations contract AI?
Organizations across industries have begun reaping the benefits of artificial intelligence. Today’s contract professionals are leveraging AI to:
- improve contract visibility;
- streamline contract data extraction and categorization;
- enjoy an intelligent clause management process;
- assess and improve risk management; and
- hold contract management employee users accountable;
Contract professionals have an exciting opportunity to automate mission-critical contract lifecycle management processes and leave time and energy to attain actionable insights and data-driven decisions. The future -- obviously bright for legal operations -- promises an enormous return on investment (ROI) of contract artificial intelligence. That’s why organizations must accelerate AI-based contract management software5 today before they can use the tools mentioned above and more.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Sean Heck is an enthusiastic content marketer and writer who has authored many articles for CobbleStone Software - an industry leader in contract management, vendor management, eSourcing, and eProcurement software. He is experienced in content writing, SEO, social media, video content generation, and more. During his stint in journalism while in university, he authored eight published works including: interviews with high-profile musicians (such as Cypress Hill, the first Latino American hip-hop group to reach multi-platinum status) and comedians (Comedy Central’s Chris DiStefano, Roy Wood Jr., Ali Siddiq); studies (such as press coverage at Philadelphia’s City Hall during the release of DA Larry Krasner’s cash-bail policy); music reviews and artist profiles.
END NOTES
- Springer Link article titled, Artificial Intelligence and Business Value: a Literature Review
- Article appearing in Google Books titled Insights You Need from Harvard Business Review (Scroll down to the section titled, The State of AI in Business by Thomas H. Davenport)
- Cobblestone software article titled Contract Management Software and Procurement Solutions
- Cobblestone VISDOM® Contract Transformation with Artificial Intelligence
- Cobblestone article titled, Take Control of Your Contracts with demo.
Other works Cited
- Enholm, I. M., Papagiannidis, E., Mikalef, P., & Krogstie, J. (2021). Artificial intelligence and business value: A literature review. Information Systems Frontiers, 1-26.
- Davenport, T. H., Brynjolfsson, E., McAfee, A., & Wilson, H. J. (2019). Artificial intelligence: The insights you need from Harvard business review. Harvard Business Press. (See also End Notes #2 above.)